
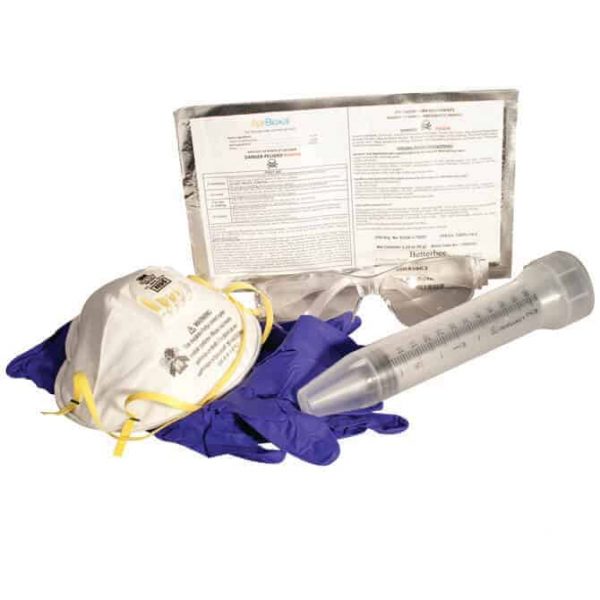
Rubber gloves and eye protection should be worn during solution preparation and application to avoid contact with skin and eyes. Trickle 5ml OA solution per bee seem, 50ml max per colony Use only as much as needed, 5 ml per bee space many times it will be less than 50ml. OA solution is applied during cooler months so the bees will typically be clustered inside the colony, making the application of the solution simple and quick.

Using a syringe, OA solution is trickled directly onto the bees along the top of each bee space, about 5ml of OA solution per bee space. No colony should receive more than 50 ml of OA. Evidence shows that concentrations higher than 3.5% do not necessarily result in increased efficacy against varroa mites and could cause harm to the bees. For example, one liter of oxalic acid solution will treat 20 colonies.

Prepare the appropriate amount of solution based upon how many colonies you have. The solution can be left at room temperature for several days if used promptly and kept refrigerated for several months. Be sure to place stored OA solution in a sealed and labeled container. All the crystals must be completely dissolved, which may require vigorous shaking. The crystals dissolve best if the sugar syrup is warm. Preparation of 3.5% OA solution: To prepare a 3.5% OA solution, measure one liter of sugar syrup and stir in 35 g of OA crystals until it is completely dissolved. Preparation of 1:1 sugar syrup by weight: Dissolve one pound sugar (2.27 US cups) in 1 pound of water (16 fluid ounces). Preparation of 1:1 sugar syrup by volume Dissolve 1/2 liter of sugar (17 ounces) in 1/2 liter of water (17 ounces) Total volume Heating fructose at high temperatures releases a chemical (hydroxymethylfurfural) that is toxic to bees. However, heat the water before the sugar is added to avoid heating the sugar. Sugar syrup solution can be prepared using a microwave or stove top. Preparation of 1:1 sugar syrup by volume: Half fill your container with sugar, add warm water to fill the container, and stir or shake until the sugar is completely dissolved and the solution is clear. The trickle method is applied to colonies through a 60ml syringe using a solution with 3.5% oxalic acid dihydrate crystals to a 1:1 sugar to water ratio. Granulated sugar should be used, not powdered sugar.
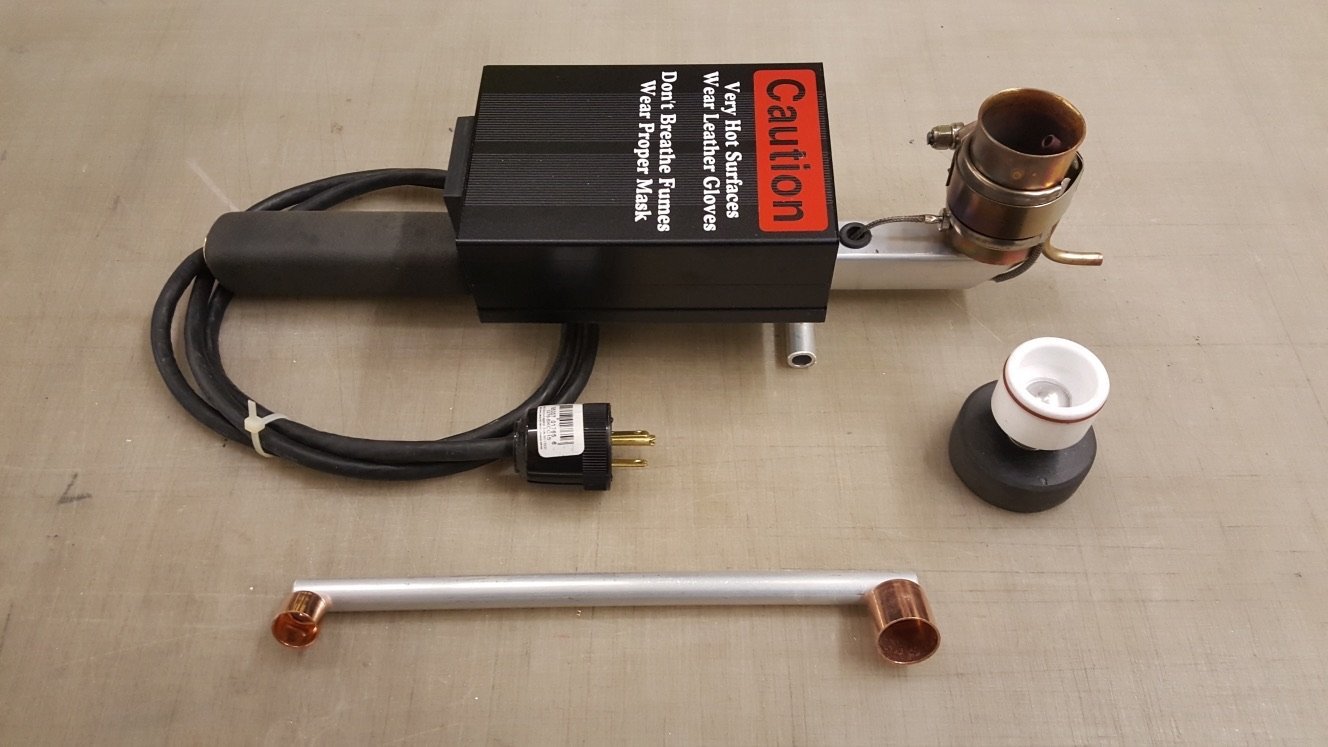

1).īefore applying OA to colonies, please keep in mind the following recommendations: However, results from our research group have shown that the vaporization method leads to higher mite drops than the trickle method (Fig. The trickle method is the most popular one in Europe and Canada because it is cost effective and easy to use. The three most common modes of oxalic acid (OA) applications are the trickle (also called dribble), spraying and vaporization methods. It is therefore recommended for broodless colonies, during winter months or in the spring before the queen starts laying eggs. OA kills phoretic mites in the colony but it cannot penetrate capped cells. It was legalized in 2015 but, it has been legal in Canada since 2010 and in Europe for over 20 years. OA is becoming a popular method for varroa mite control in the US. Although it is considered an organic chemical, it is highly corrosive and causes severe burns if used improperly. Oxalic acid dihydrate (OA) (also known as wood bleach) is an organic acid naturally found in plants including spinach, rhubarb, black tea, and honey.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
